Electromagnetic Polarizaiton
Radio waves consist of an electric field wave and a magnetic field wave at right angles to one another as shown in the diagram below:
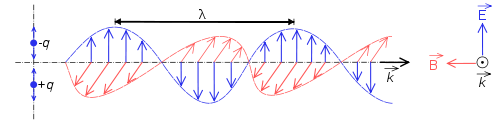
The blue lines labeled E represent the electric field and the red lines labeled B represent the magnetic field. The direction that the electric field oscillates in is typically called the direction of the polarization of the electromagnetic wave. The direction that the electric field oscillates corresponds to the direction that the antenna runs with respect to the earth. So, for a vertical antenna projecting straight up from the ground, we say that the wave is vertically polarized, and for a dipole antenna running parallel to the ground, we say that the wave is horizontally polarized.
Along a line of sight transmission path, where nothing else if effecting the polarization of the wave, the best reception can be gained by orienting the receiving antenna so that it has the same polarization as the transmitting antenna. For skip communications, the polarization of the original radio wave is randomized as it reflects between the earth and ionosphere. When listening to satellite signals, you might observe a periodic fading of the signal. This is caused by the same phenomena. As the satellite rotates, the polarization of its antenna changes with respect to your receiving station.
Exam Questions
Which of the following describes a simple dipole mounted so the conductor is parallel
to the Earth's surface?
A. A ground wave antenna
B. A horizontally polarized antenna
C. A rhombic antenna
D. A vertically polarized antenna
Which of the following is true regarding vertical antennas?
A. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the Earth
B. The electric field is perpendicular to the Earth
C. The phase is inverted
D. The phase is reversed
What can happen if the antennas at opposite ends of a VHF or UHF line of sight radio
link are not using the same polarization?
A. The modulation sidebands might become inverted
B. Signals could be significantly weaker
C. Signals have an echo effect on voices
D. Nothing significant will happen
Which of the following is a common effect of "skip" reflections between the Earth and
the ionosphere?
A. The sidebands become reversed at each reflection
B. The polarization of the original signal is randomized
C. The apparent frequency of the received signal is shifted by a random amount
D. Signals at frequencies above 30 MHz become stronger with each reflection
What causes "spin fading" when referring to satellite signals?
A. Circular polarized noise interference radiated from the sun
B. Rotation of the satellite and its antennas
C. Doppler shift of the received signal
D. Interfering signals within the satellite uplink band